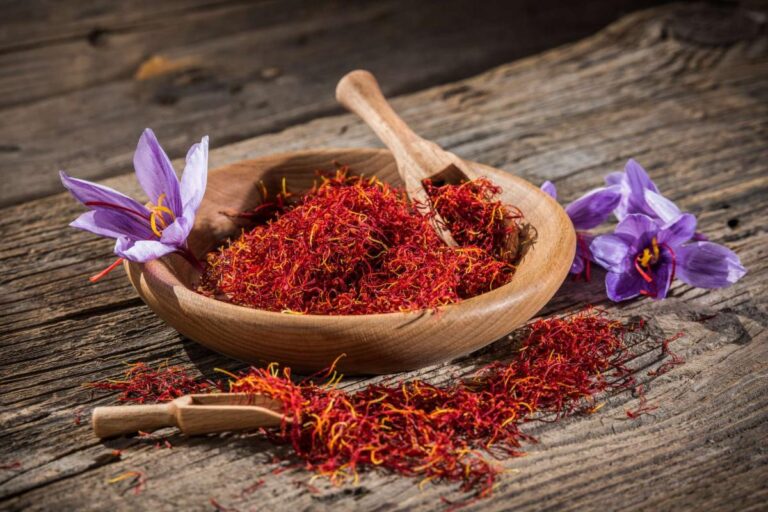
Saffron is a spice derived from the flower of Crocus sativus, commonly known as the saffron crocus. It’s known for its distinctive flavor, aroma, and vibrant color.
If you’re considering using saffron or any other supplement while taking Fildena 200 and Malegra 200 (a medication containing sildenafil used to treat erectile dysfunction), it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before combining the two.
Saffron has been used for culinary and medicinal purposes for centuries, and it contains several bioactive compounds that are believed to offer potential health benefits.
Here are some potential health benefits of saffron:
Antioxidant Properties:
Saffron contains antioxidants like crocin, crocetin, and safranal, which help protect cells from oxidative stress and free radical damage. Antioxidants are important for overall health and may contribute to reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Saffron contains several bioactive compounds that contribute to its antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are substances that help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can lead to cell damage and contribute to various chronic diseases.
Antioxidants in saffron can help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress. This protection is important for overall cellular health and may contribute to a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Oxidative stress is linked to aging and the degeneration of cells over time. Antioxidants can help slow down the aging process by preventing cellular damage.
Antioxidants in saffron may contribute to heart health by protecting blood vessels and reducing inflammation, which are important factors in cardiovascular diseases.
It may support brain health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially contributing to improved cognitive function and a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Mood Enhancement:
Some studies suggest that saffron may have mood-enhancing properties and could be beneficial for individuals with mild to moderate depression. It’s thought to influence neurotransmitter levels, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play a role in mood regulation.
Saffron compounds may have an impact on neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers in the brain that regulate mood.
These compounds could potentially affect the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play a role in mood regulation.
The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties of saffron may contribute to reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, both of which are implicated in mood disorders.
Some studies suggest that saffron may help reduce stress and anxiety levels. By promoting relaxation and reducing stress, saffron might indirectly improve mood.
Memory and Cognitive Function:
Saffron’s bioactive compounds may have cognitive-enhancing effects. Some research indicates that saffron supplementation could potentially improve memory and cognitive function, particularly in older adults.
The antioxidants in saffron, particularly crocin, and crocetin, may help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, which are factors that contribute to cognitive decline.
Saffron compounds may influence the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, including serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine, which play roles in memory and cognitive function.
Some research suggests that saffron might enhance blood flow to the brain, improving the delivery of oxygen and nutrients that support cognitive health.
If you’re interested in using saffron to support memory and cognitive function, consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation. They can provide personalized guidance based on your health status and needs.
Cognitive health is influenced by a range of factors, including diet, physical activity, sleep, and mental stimulation. Saffron, if used, should be part of a comprehensive approach to cognitive well-being.
Eye Health:
Saffron contains compounds that are beneficial for eye health, including carotenoids like crocin. These compounds may help protect the retinal cells from damage and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
The antioxidants in saffron, especially crocin, have been studied for their potential to protect retinal cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress plays a role in the development of AMD.
Saffron compounds may help improve blood flow to the retina, which is important for delivering oxygen and nutrients to retinal cells.
If you have concerns about your eye health or are at risk of eye conditions like AMD, it’s important to consult an eye care professional (ophthalmologist or optometrist) before considering saffron supplementation. Regular eye exams and professional guidance are essential for maintaining eye health.
If you’re considering saffron supplements for potential eye health benefits, ensure that you’re using a reputable product with accurate dosing. Quality and purity are crucial.
Saffron, if used, should be viewed as a potential complement to professional eye care and not a substitute for it. Follow your eye care professional’s recommendations.
Eye health is influenced by various factors, including a diet rich in nutrients beneficial for the eyes (such as antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids), protecting your eyes from excessive UV exposure, and avoiding smoking.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Saffron’s bioactive compounds, including crocetin, have been studied for their potential anti-inflammatory properties. Reducing chronic inflammation is associated with a lower risk of various chronic diseases.
Saffron’s compounds, particularly crocin, and crocetin, have antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Some studies suggest that saffron may modulate the production of certain inflammatory markers, such as cytokines and enzymes, that contribute to the inflammatory response.
Saffron compounds might interfere with specific molecular pathways involved in inflammation, helping to mitigate excessive and chronic inflammation.
Saffron’s effects on the immune system may contribute to its anti-inflammatory potential. It’s believed to have immunomodulatory effects that help regulate immune responses.
Chronic inflammation is associated with various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Saffron’s anti-inflammatory effects could play a role in reducing the risk of these conditions.
Chronic inflammation is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Saffron’s potential anti-inflammatory effects could be beneficial for brain health.